- By definition, one atom of carbon-12 is assigned a mass of exactly 12 atomic mass units (amu). An atomic mass unit is defined as a mass equal to one twelfth of an atom of carbon-12. The mass of any isotope of any element is expressed in relation to the carbon-12 standard. For example, one atom of helium-4 has a mass of 4.0026 amu.
- Atomic Mass One atomic mass unit (amu): the mass exactly equal to one-twelfth the mass of one carbon-12 atom that has six protons and six neutrons. 1 atom of carbon-12 = 12 amu 1 amu = mass of one C-12 atom 12 1 amu = 1.66054 x 10-24 g and 1 g = 6.02214 x 1023 amu Average Atomic Mass: the weighted average of the masses of the naturally occurring.
- Average atomic mass for each element. In order to calculate this quantity, the natural abundance and atomic mass of each isotope must be provided. Consider the individual atomic masses for magnesium isotopes given in Model 2. Which isotope has an atomic mass closest to the average atomic mass listed on the periodic table?
How do you calculate the atomic mass of carbon?
The average atomic mass of carbon is 12.011 amu. Assuming you were able to pick up only one carbon atom, the chance that you would get one with a mass of 12.011 amu is. Answer is: the average atomic mass of carbon is 12.011 amu. M(¹²C) = 12.00 amu; the average atomic mass of carbon-12. M(¹³C) = 13.003354 amu; the average atomic mass of carbon-13.
1 Answer
The term 'atomic mass' refers to the mass of a single atom. The mass of a single atom of carbon-12 is defined as exactly 12 u.
The term atomic mass is also often used (though technically, incorrectly) to refer to the average atomic mass of all of the isotopes of an element.
Average Atomic Mass Of Carbon 12
This second definition is actually the relative atomic mass of an element — a single average value of the element's mass based on the masses of its isotopes.


Carbon has 15 known isotopes, of which only two (
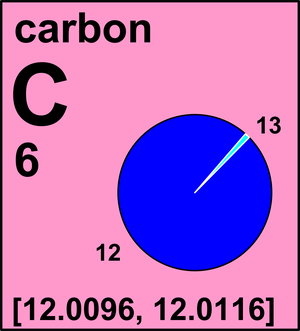
Carbon consists of 98.93%
METHOD 1
To find the average atomic mass, you take a certain number of atoms, find the total mass of each isotope, and then divide the total mass of all the atoms by the total number of atoms.
Assume that you have, say, 10 000 atoms of carbon. Then you have 9893 atoms of
Average Atomic Mass Of Carbon In Amu

METHOD 2
Another way of determining the average mass is to multiply the atomic mass of each isotope by its percentage and then add the numbers.
The two methods are mathematically equivalent. Thus,
Method 2 is probably mathematically simpler, but Method 1 makes it clear that you are determining an average mass.
Choose the method that you prefer.
Average Atomic Mass Of Carbon-12
Related questions
